Business Process Management
Business Process Management 101
According to leading analyst firm Gartner, business process management is “a management discipline that treats business processes as assets that directly improve enterprise performance by driving operational excellence and business agility.” At its core, business process management is an approach to improve the processes and workflows within an organization. A business process can be anything from ordering materials and delivering goods to making strategic decisions and managing a department or organization.
Ideally, business process management would enable an organization to reach new levels of efficiency and effectiveness, while at the same time to become more flexible and agile to change. So, how does business process management achieve this?
The goal of business process management is to provide an understanding of an organization and its performance; this is often achieved by providing actionable information in real-time. In this sense, BPM can be thought of as being related to business intelligence and operational intelligence solutions. With this actionable information in hand, key stakeholders within an organization can understand the relationship between processes and model them out, gaining visibility into key areas and finding opportunities for improvement. Technology is often implemented to gather and model this information; technology is often also used to automate business processes, resulting in the elimination of inefficient and tedious manual processes.
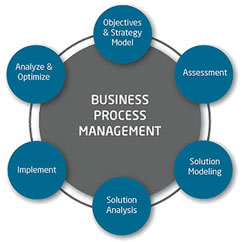
The BPM Lifecycle
 The business management lifecycle encompasses:
The business management lifecycle encompasses:
- Process Design: identifying existing processes and designing new ones
- Modeling: running “what-if” analyses and introducing variables into the process design to determine how processes will operate
- Execution: carrying out the required steps of the process and developing or acquiring any necessary applications
- Monitoring: tracking individual processes and their results
- Optimization: analyzing results to identify issues and any potential opportunities for improvement
- Re-engineering: reconfiguring processes if they become too complex or do not deliver the desired value
What are the Benefits of Business Process Management?
Business process management provides organizations with a systematic way to model and analyze their processes, resulting in benefits such as:
- Visibility into organizational activity
- Ability to identify bottlenecks
- Ability to identify areas to improve and optimize
- Lower lead times
- Defined roles and responsibilities for staff
- Automated processes, leading to productivity gains
Ultimately, these benefits empower businesses to respond and act upon changing market demands, giving them a competitive advantage.
BPM Suites
There are a number of BPM suites available on the market built to enable and support continuous process improvement. Business process management is often broken down into a service pattern that provides a guide for how the applications built into a BPM Suite should function.
This service pattern is broken down into several layers that include:
- The user interface layer, which may be provided by the BPM software or may be a custom interface that works with the BPM solution
- The BPM tools layer, which provides the core functionality
- The storage layer, which is a repository for corporate data and business process models
- The interface layer, which exchanges data with the BPM suite
Most business process management suite (BPMS) vendors provide process analysis, design, and workflow modeling tools within their suites. According to Gartner, most organizations choose to invest in a BPMS because they need support for a program of continuous process improvement, support for a business transformation project, and/or support for a service-oriented architecture (SOA), process-based redesign. Organizations may also look to adopt a BPMS to guide their implementation process for an industry-specific or company-specific process solution.
According to research conducted by Gartner, the leading vendors providing BPMS include Active Endpoints, Adobe, AgilePoint, Appian, BizAgi, Cordys, EMC, Fujitsu, and others, which are listed in the Magic Quadrant below.

BPM solutions have primarily been adopted by financial organizations, where visibility and adherence to compliance regulations are an integral part of this sector. BPM has also been implemented within service organizations where staff productivity and effectiveness play a key role in process performance. Most organizations decide to adopt BPM because they anticipate that process changes will occur frequently. However, with the current economic downturn, many organizations are also beginning to look further into BPM as an opportunity to transform their business, improve processes, and cut costs.
Want more on Business Process Management? Find the best BPM software in the industry with Business-Software.com’s Top 10 Business Process Management Software report. For additional reading material, check out the Business Intelligence resource page.






